The Spanish Alphabet || From Greek Ancient Times to the 21st Century
🇪🇸 The Spanish Alphabet
A World Unto Itself 🌏
📖 The actual term “alphabet” (in Spanish alfabeto ) derives from the Greek word alphabētum
But Spanish is a Latin-derived language, right? So what’s up with that?
Alfabeto (a word coined using the first two letters of the Greek alphabet – alpha, beta), refers to the more general concept of the alphabet, as in, the notion of a series of sequential letters used to graphically represent an alphabet written language.

There is however a second more specific term in Spanish used to refer to the Spanish, Latin derived alphabet, which is, abecedario .
The word abecedario was coined using the first four letters of the Latin alphabet sequence (a, be, ce, de), hence it is more specific to Spanish, as a Latin-derived language that uses Latin characters in its written form.
👉 So, in conclusion, while both Spanish words, alfabeto and abecedario, are correct and synonymously translate to “alphabet”, the first one refers to the general notion, while the second is more specific to Latin derived languages, Spanish among them.
🇪🇸 Let’s break down the ‘Spanish Alfabeto’ with us!
Spanish Alphabet || The Spanish ABCDs, Not Your Typical ABCs
Spanish Alphabet || ABCDs and Beyond, The Spanish Alphabet and the Digraphs
Spanish Alphabet || When We Were 29 in the Spanish Alphabet
Spanish Alphabet || The Origins, It All Started in Greece
Spanish Alphabet || FAQs
Spanish Alphabet || The Spanish ABCDs, Not Your Typical ABCs
“Let’s start from the very beginning, a very good place to start. When you read you begin with A, B, C…”. 📖
🔔 Does this ABCs chant ring a bell? Sound of Music?
But in Spanish, it would be the A, B, C, D (ABCDs) as the word itself abecedario (in English, alphabet) indicates, referencing the first four letters of the Latin alphabet sequence.
➡️ Following the baby steps philosophy, let’s start from the very beginning of the Spanish alphabet, which is now formed by the 27 letters (English has 26) listed below sequentially.
| a, A a | b, B be | c, C ce | d, D de | e, E e | f, F efe | g, G get | h, H hache | i, I i |
| j, J jota | k, K ka | l, L ele | m, M eme | n, N ene | ñ, Ñ eñe | o, O o | p, P pe | q, Q cu |
| r, R erre | s, S ese | t, T te | u, U u | v, V uve | w, W uvedoble | x, X equis | y, Y ye | z, Z zeta |
👉 Each letter listed sequentially has the recommended pronunciation in Spanish by the Real Academia Española, the foremost authority in the Spanish language.
Although said institution admits other pronunciations – especially those traditionally used in other Spanish-speaking countries – it recommends this unified form of pronunciation, particularly when it comes to teaching and communications.

Months in Spanish 📆 || Key Vocabulary and Cultural Insights
Learn How to Say the Months in Spanish and Find Out How Spaniards Spend the Year No matter if you’re talking about birthdays, business trips or holiday plans, months are essential vocabulary you need to know in Spanish. So in…
Spanish Alphabet || ABCDs and Beyond, The Spanish Alphabet and the Digraphs
Did you know? In Spanish, there is more than just a sequential twenty-seven letter alphabet. Yes, there is more to it!
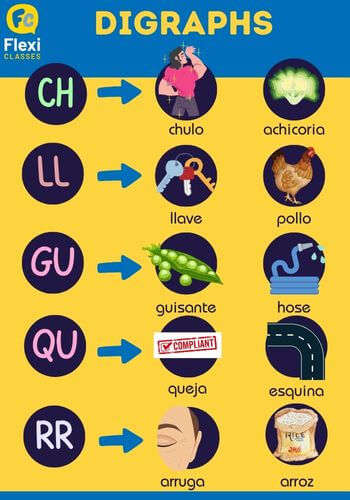
☀ There are five additional digraphs. And what are digraphs? Digraphs are the combination of two letters used to graphically represent certain single units of sound (phonemes) in a language, kind of like a sound bit representation.
In Spanish, there are five distinct categories of digraphs. These digraphs, although they do not actually form part of the Spanish alphabet, add a particular twist to it, as they form a unique way of pronouncing two combined letters:
a. The digraph ch represents the phoneme /ch/, used in words such as chulo (boastful), achicoria (chicory), chiste (joke).
b. The digraph ll represents the phoneme /ll/, used in words such as lluvia (rain), llave (key), pollo (chicken).
c. The digraph gu represents the phoneme /g/ before e or i, used in words such as guisante (pea), guerra (war), manguera (hose).
d. The digraph qu represents the phoneme /k/ before e or i, used in words such as quinina (quinine), queja (complaint), esquina (corner).
e. The digraph rr represents the phoneme /rr/, used in words such as arruga (wrinkle), arroz (rice), borrar (erase).
Spanish Alphabet || When We Were 29 in the Spanish Alphabet
As early as 1754 and up until 2010, ch and ll were considered as letters part of the Spanish alphabet, raising the total count to 29.
As part of the normal evolution of a language, in 2010, ch and ll were formally dropped from the formal category as letters of the Spanish alphabet. They were thereafter considered as digraphs, deciding to follow the same standards as all of the other written alphabet languages, that only considered letters as such when they were single graphic symbols.
👉 So, at the drop of a hat, the Spanish alphabet was shortened, from 29 to these 27 letters:

📌 Fact: Wherein letters or graphemes are the smallest unit possible of the graphic system or written alphabet.
Spanish Alphabet ||
The Origins, It All Started in Greece

Spanish is a Latin-derived language, that we know. What is not as commonly known is that the sequence of letters used by the Romans in their written language, Latin, actually derives from the Greek alphabet, although not directly but through the Etruscans.
📌 Did you know? The Etruscans settled in the Italian Peninsula in the earlier part of the first millennial A.D. and their language (a variant of the Greek alphabet) greatly influenced the early Romans (initially called Latins).
The initial Latin alphabet was composed of 21 letters, all CAPS!
A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I, K, L, M, N, O, P, Q, R, S, T, V, X.
After Rome conquered Greece, around the mid-2nd century A.D., the Greek influence in Rome increased notably, hence many Greek words were borrowed by the Latin language.
This meant that new letters had to be incorporated into the Latin alphabet to be able to write these new “foreign” words. Basically, the letters Y and Z were added to the Latin language, increasing the count to 23 letters around the 1st Century A.D, as listed below:
A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I, K, L, M, N, O, P, Q, R, S, T, V, X, Y, Z.
All of the above letters, in the same sequence, form part of the Spanish alphabet, with a few additions incorporated over the years.
These new introductions were primordially out of necessity to represent new sounds (technically, phonemes) that were inexistent in Latin or that were introduced into the Spanish language as borrowed terms from foreign languages.
Still, we are 4 letters short to get the actual count of 27 letters. Over time, four new letters were incorporated into the Spanish alphabet (which were not part of the initial Latin alphabet): u, j, ñ, w.
These “new” letters per se were not strictly speaking novelle symbols but really just graphic adaptations or combinations of other preexisting letters.
🔁 And looping back to where we started, that leads us to the current day 27 letter Spanish alphabet:
a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h, i, j, k, l, m, n, ñ, o, p, q, r, s, t, u, v, w, x, y, z.
Now you’ve mastered the alphabet, why not check out these Spanish essentials?
👉 How to Say Nice to Meet You in Spanish
Spanish Alphabet || FAQs
How many letters are there in the Spanish Alphabet?
The Spanish alphabet, synonymously referred to in Spanish as el alfabeto or el abecedario, has 27 letters, sequentially listed as follows:
a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h, i, j, k, l, m, n, ñ, o, p, q, r, s, t, u, v, w, x, y, z.
The inventory of letters in the Spanish alphabet has the same 26 letters as the English one, with the addition of the letter ñ, a distinctively Spanish symbol that even the name of the country carries, España.
Are ch and ll letters in the Spanish alphabet?
Up until 2010 ch and ll were considered as letters integrating the Spanish alphabet, which then had a total count of 29 letters.
However, ch and ll were permanently excluded from the Spanish alphabet in 2010 on the account that, in fact, they were not actually letters in the strict sense of the word but digraphs.
Digraphs are a combination of two letters used to represent a phoneme (a single unit of sound in a language, used to phonetically distinguish one word from another).
So, initially, ch and ll were alphabetized separately and thereafter, any words that started with these digraphs – such as chica (girl) and lluvia (rain) – were categorized under the c and l respectively.
What is the difference between alfabeto and abecedario?
While both words, alfabeto and abecedario synonymously refer to the term “alphabet”, the first one, refers to the general notion of the term alphabet, as it derives from the Greek word alphabētum (alpha and beta being the first two letters of the Greek alphabet.
While abecedario, is a term more specific to Latin-derived languages (Spanish among them), as it is a word coined using the first four letters of the Latin alphabet (a, be, ce, de).
What is the origin of the ñ?
The letter ñ, unique to the Spanish alphabet, originated as the abbreviation of the digraph nn back in medieval times, to represent the nasal palatal sound /ñ/, which was non-existent in Latin.
(Grammar review: digraphs are the combination of two letters used to graphically represent a single sound in a language, kind of like a sound bit representation of a letter).
Fun fact: In Spanish, the little twirly that crowns the ñ – which in proper English is referred to as the “tilde” – is called virguilla.
Truly, the ñ is a genuinely Spanish letter.
What are the special characters in Spanish?
There are several special characters that the Real Academia Española (the foremost authority in the Spanish language) acknowledges to be part of the Spanish written language.
Those that refer to the Spanish accent marks are called diacritic symbols (signos diacríticos), a graphic symbol added onto a letter, which then confers a special value to said letter (basically altering or stressing its pronunciation).
Diacritic symbols can be distinguished into two main categories: the diéresis (in English the trema symbol) used over the u vowel in Spanish like so, ü and the tilde (which then subdivides into two subcategories, the virguilla (the tilde over the ñ) and the acute accents (á, é, í, ó, ú).
Examples of each:
Use of diéresis or trema symbol: vergüenza (shame), pingüino (penguin), bilingüe (bilingual)
Use of virguilla (in English the tilde symbol): España, niño (boy), año (year)
Use of tilde or acute accent:
á: Árabe (Arab), sábanas (sheets), cáscara (shell/peel)
é: miércoles (Wednesday), médico (doctor), sartén (skillet)
í: país (country), mediodía (noon), raíz (root)
ó: evolución (evolution), atónito (astonished), balón (ball)
ú: público (public), común (common), champú (shampoo)]
Want More From LTL?
FANCY LEARNING SPANISH? Check out our online Spanish courses here.
We offer a 7-day free trial to all online students where you can study Spanish 24/7. It doesn’t end there either.
We teach over 10 of the world’s most popular languages 😎
Come and be a part of our amazing community.