Fruits and Vegetables in Spanish: Essential Vocabulary
Fruits and Vegetables in Spanish: Seasonal Varieties, Categories and Basic Vocabulary
Spain is considered el huerto de Europa (the garden of Europe) due to its vast agricultural production, especially of fruits, and vegetables, supplying many European countries.

The Spanish Mediterranean climate, vast farmlands and well-developed infrastructure have made Spain one of the top exporters of fresh produce in Europe, supplying local markets as well with a wide variety of seasonal and year-round fruits and vegetables.
So, whether you are in Spain buying produce at a market or a supermarket, considering your options on a restaurant menu, or following a recipe in Spanish, some basic veggie and fruit lexicon in Spanish will help keep you well nourished!
But first, fruit in Spanish is fruta and vegetable is verdura
Fruits and Vegetables in Spanish || Basic Fruit and Vegetable Vocabulary
Fruits and Vegetables in Spanish || Fruit and Vegetable Categories
Fruits and Vegetables in Spanish || Winter Produce
Fruits and Vegetables in Spanish || Spring Produce
Fruits and Vegetables in Spanish || Summer Produce
Fruits and Vegetables in Spanish || Autumn Produce
Fruits and Vegetables in Spanish || FAQs
Fruits and Vegetables in Spanish || Basic Fruit and Vegetable Vocabulary
Before we take a bite into the specific kinds of common produce in Spain, here are some basic fruit and vegetable-related vocabulary that can help simplify how you refer to them.
De temporada (Seasonal), refers to fruits and vegetables available during a particular season (spring, summer, autumn, and winter).
CosechaHarvest
Verduras and hortalizas are often used interchangeably to refer to vegetables. Verdura refers mostly to green or leafy vegetables, while hortaliza is used more broadly to refer to any edible plant. However, the term verdura is commonly used as a general term for vegetables.
| SPANISH | ENGLISH |
|---|---|
| Frutas | Fruits |
| Ecológico | Organic, grown without synthetic chemicals |
| De proximidad | Locally sourced, refers to products produced locally and within a close geographical area |
| Invernadero | Greenhouse |
| Maduro | Ripe |
| Verde | Literally means “green” and refers to not fully ripened fruits and vegetables |
| Pasado | Overripe, a common way to describe fruits or vegetables that have ripened past their optimal state of consumption or Demasiado maduro (too ripe). |
| Fresco | Fresh |
| Congelado | Frozen |
| En conserva | Canned, refers to food preserved in a can |
| Dulce | Sweet |
| Amargo | Bitter |
| Agrio | Sour |
| En su punto | Peak ripeness, in this context refers to fruits and vegetables that are in their ideal state for consumption, perfectly ready to eat, and just right. |
| Crujiente | Crunchy |
| Jugoso | Juicy |
Fruits and Vegetables in Spanish || Fruit and Vegetable Categories
Seasonality aside, fruits and vegetables can also be grouped according to the following categories.
Categories of Vegetables
| spanish | english | exampleS |
|---|---|---|
| Tubérculos | Tubers |
patatas
(potatoes),
boniato
(sweet potato), yuca (cassava) |
| Hortalizas de hoja | Leafy greens |
espinacas
(spinach), acelgas (Swiss chard), lechuga (lettuce) |
| Bulbos | Bulbs |
cebolla
(onion), ajo (garlic), puerro (leek) |
| Raices | Roots |
zanahoria
(carrot), rábano (radish), remolacha (beet) |
| Frutos | Fruiting vegetables |
tomate
(tomato), pimiento (bell pepper), calabacín (zucchini) |
| Crucíferas | Cruciferous vegetables |
brócoli
(broccoli), coliflor (cauliflower), repollo (cabbage) |
| Tallos | Stalk or stem vegetables |
espárragos
(asparagus), apio (celery), ruibarbo (rhubarb) |
| Semillas | Seeds |
guisantes
(peas), maíz (corn), habas (fava beans) |
Categories of Fruits
| SPANISH | ENGLISH | EXAMPLE |
|---|---|---|
| Cítricos | Citrus fruits | limón (lemon), naranja (orange), pomelo (grapefruit) |
| Bayas | Berries | fresa (strawberry), arándano (blueberry), mora (blackberry) |
| Frutas de hueso | Stone fruits | melocotón (peach), cereza (cherry), ciruela (plum) |
| Frutas de pepita | Pome fruits | pera (pear), manzana (apple), uva (grape) |
| Frutas tropicales | Tropical fruits | piña (pineapple), mango (mango), maracuyá (passion fruit) |
| Frutos secos | Nuts and seeds, botanically considered fruits | almendras (almonds), avellanas (hazelnuts), nueces (walnuts) |
| Frutas deshidratadas / Frutas secas | Dehydrated fruits or Dried fruits | pasas (raisins), dátiles (dates), higos secos (dried figs) |

Food in Spanish || Essential Vocabulary & Must-Eat Dishes
Spanish Food Vocabulary || And The Million Dollar Question: What Time Do People Eat in Spain? Spain is Different- once a national slogan. True to that phrase, you’re going to need some adjustments when it comes to mealtimes in Spain….
Fruits and Vegetables in Spanish || Winter Produce
Winter produce consists mainly of hearty greens and citrus fruits.
Vegetables
| SPANISH | ENGLISH |
|---|---|
| Acelgas | Swiss chard |
| Repollo | Cabbage |
| Coles de Bruselas | Brussel sprouts |
| Zanahoria | Carrot |
| Calabaza | Pumpkin |
| Puerros | Leeks |
| Nabos | Turnips |
Fruits
| SPANISH | ENGLISH |
|---|---|
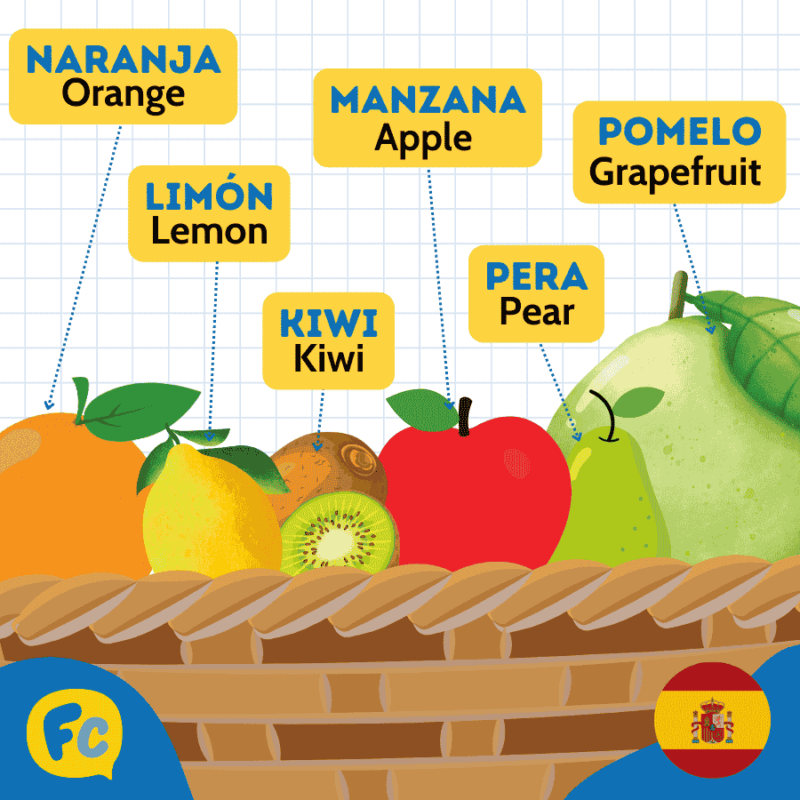
| Naranja | Orange |
| Limón | Lemon |
| Manzana | Apple |
| Kiwi | Kiwi |
| Pera | Pear |
| Pomelo | Grapefruit |
Fruits and Vegetables in Spanish || Spring Produce
Although some seasonal fruits can be found all year round as they are harvested in greenhouses, these are some of the typical spring produce:
Vegetables
| SPANISH | ENGLISH |
|---|---|
| Alcachofas | Artichokes |
| Espárragos | Asparagus |
| Espinacas | Spinach |
| Guisantes | Peas |
| Habas | Fava beans |
| Judías verdes | Green beans |
Fruits
| SPANISH | ENGLISH |
|---|---|
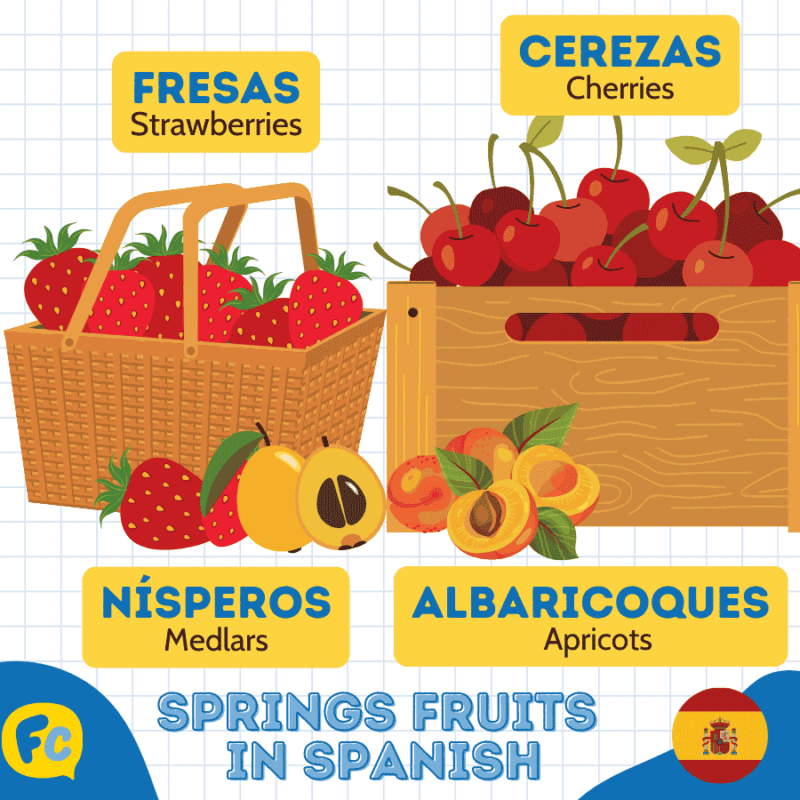
| Fresas | Strawberries |
| Cerezas | Cherries |
| Nísperos | Medlars |
| Albaricoques | Apricots |
Fruits and Vegetables in Spanish || Summer Produce
Summer produce brings sun-ripened vegetables and vibrantly colored and refreshing fruits
Vegetables
| SPANISH | ENGLISH |
|---|---|
| Pepino | Cucumber |
| Calabacín | Zucchini |
| Tomate | Tomato, although botanically classified as a fruit, is considered a vegetable in culinary terms |
| Pimiento | Bell pepper |
| Berenjena | Eggplant |
| Patatas | Potatoes, although they can be found all year round, the main season is from summer to early autumn. |
Fruits
| SPANISH | ENGLISH |
|---|---|
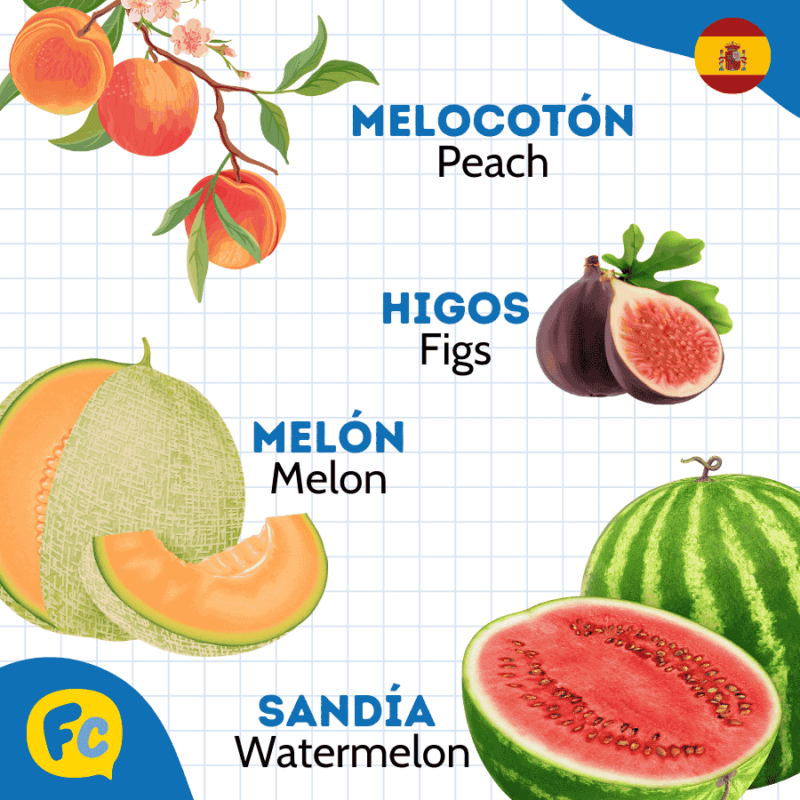
| Melocotón | Peach |
| Melón | Melon |
| Sandía | Watermelon |
| Higos | Figs |

Spanish Question Words // Vocab Guide & FREE QUIZ
To Get the Right Answers, You Must First Ask the Right Spanish Questions! Question words in Spanish are essential for, well, asking questions! In this blog, we’ll teach you essential vocab and break down the grammar of Spanish questions with…
Fruits and Vegetables in Spanish || Autumn Produce
As temperatures cool, autumn fruit and vegetable varieties are citrusy and earthy. While many are available in other seasons, most thrive best in the autumn and winter.
Vegetables
| SPANISH | ENGLISH |
|---|---|
| Calabaza | Pumpkin |
| Boniato | Sweet potato |
| Setas | Mushrooms, while botanically not a vegetable, are often categorized as vegetables in culinary terms. |
| Coliflor | Cauliflower |
| Brócoli | Broccoli |
| Chirivía | Parsnip |
| Col rizada | Kale |
Fruits
| SPANISH | ENGLISH |
|---|---|
| Uvas | Grapes |
| Plátanos | Bananas, although available year-round, the peak harvesting season in Spain is during the autumn and winter months |
| Castañas | Chestnuts |
| Nueces | Walnuts |
| Aceitunas | Olives |
| Granada | Pomegranate |
| Caquis | Persimmons |
Fruits and Vegetables in Spanish || FAQs
What is the difference between verdura and hortaliza?
Verduras and hortalizas are terms often used interchangeably to refer to “vegetables”. Strictly speaking though, the word verdura usually refers to green or leafy vegetables, while hortaliza is used in a broader sense to refer to any edible plant.
However, verdura is commonly used as a general term for vegetable in everyday speech.
What fruits are most consumed in Spain?
In Spain, Oranges have the highest per capita consumption, followed by bananas. According to 2021 statistics, oranges had a per capita consumption of 15.1 kilograms, while bananas amounted to 13.5 kilograms per capita.
What fruits are native to Spain?
Some fruits native to Spain or commonly cultivated in Spanish soil include:
Níspero (Medlar), widely cultivated in the Mediterranean regions, including Spain
Aceitunas (Olives), Spain is one of the world’s biggest producers of olive oil
Granada (Pomegranate), as the name indicates, this fruit is widely grown in the south of Spain, particularly in the province of Granada.
Pera de conferencia (Conference pear), a variety of pear native to Spain.
Membrillo (Quince)
Chirimoya (Cherimoya), while this fruit originated from the Andean regions of South America, has been cultivated in the south of Spain for centuries.
What is the difference between olivas and aceitunas?
According to the Real Academia Española dictionary, aceituna and oliva both refer to the fruit of the olive tree, “olive”. However, their usage varies regionally and contextually.
While aceituna is more commonly used in Spain, the word oliva is more frequently used in some areas such as Cataluña and Aragón. Also, in certain contexts, the term aceituna is preferred, particularly when referring to olives that are consumed as food.
On the other hand, oliva is used instead when referring to or relating to olive oil. Notice how olive oil translates to aceite de oliva and not aceite de aceituna.
What is the difference between ecológico and orgánico in Spanish?
The Spanish word for organic is ecológico, which is a broader term for food grown without synthetic chemicals. The word orgánico in Spain is more closely associated with organic certification, which implies adherence to pre-established farming standards and practices.
Want More From LTL?
FANCY LEARNING ITALIAN? Check out our online Italian courses here.
We offer a 7-day free trial to all online students where you can study Italian 24/7. It doesn’t just end with Italian.
Come and be a part of our amazing community.